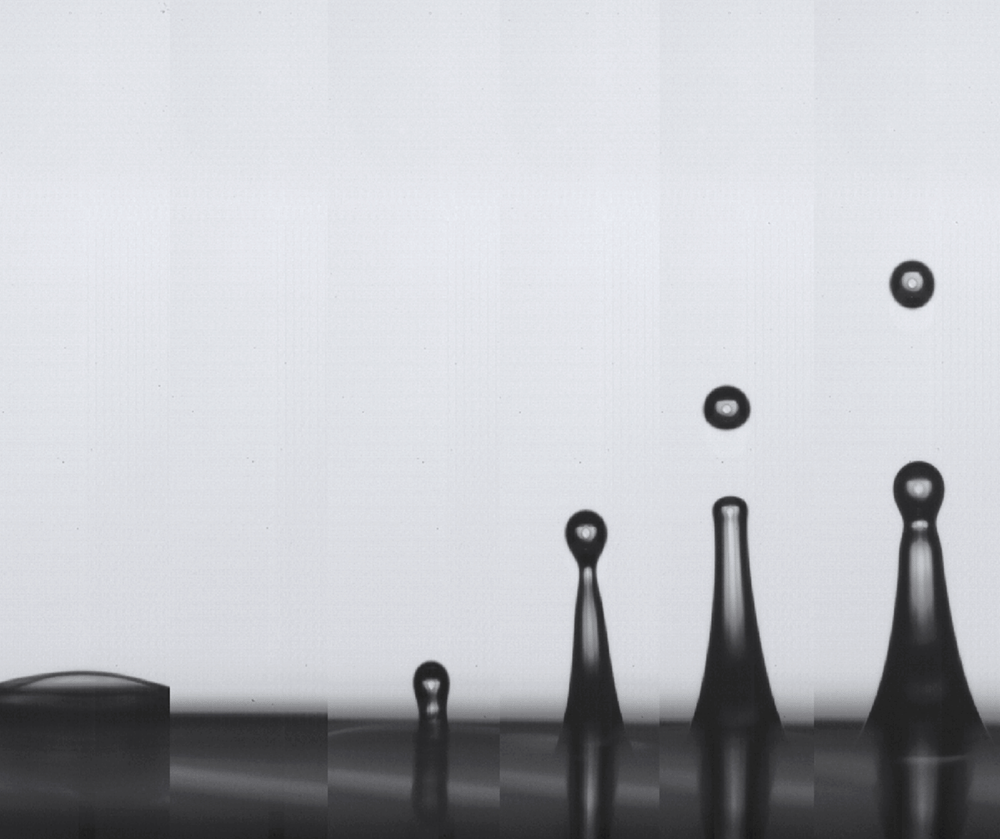
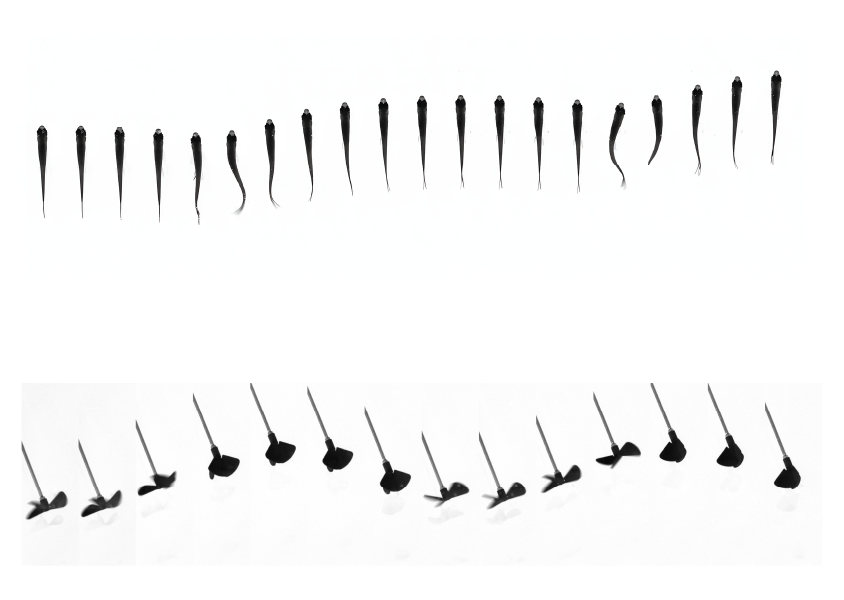
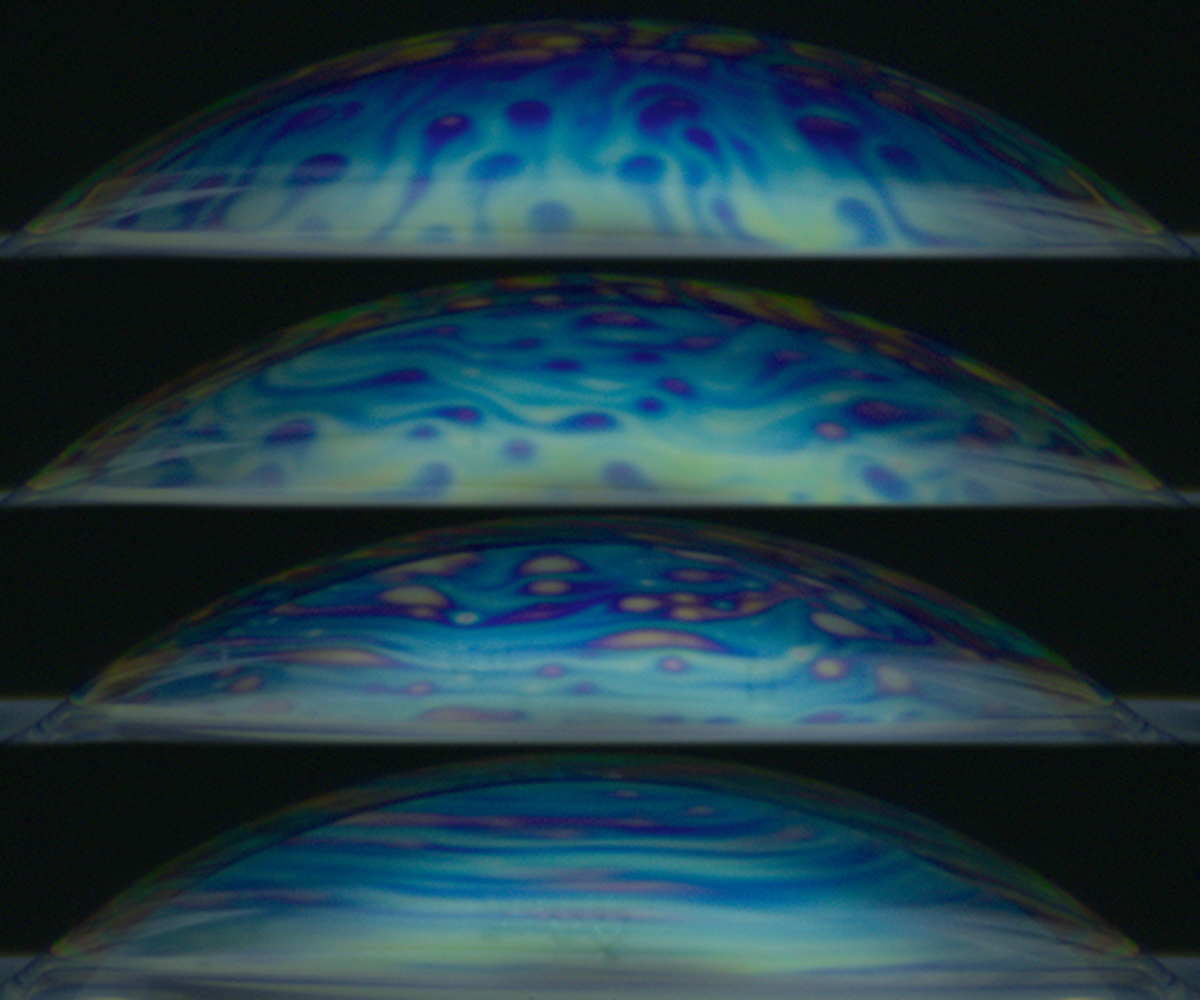
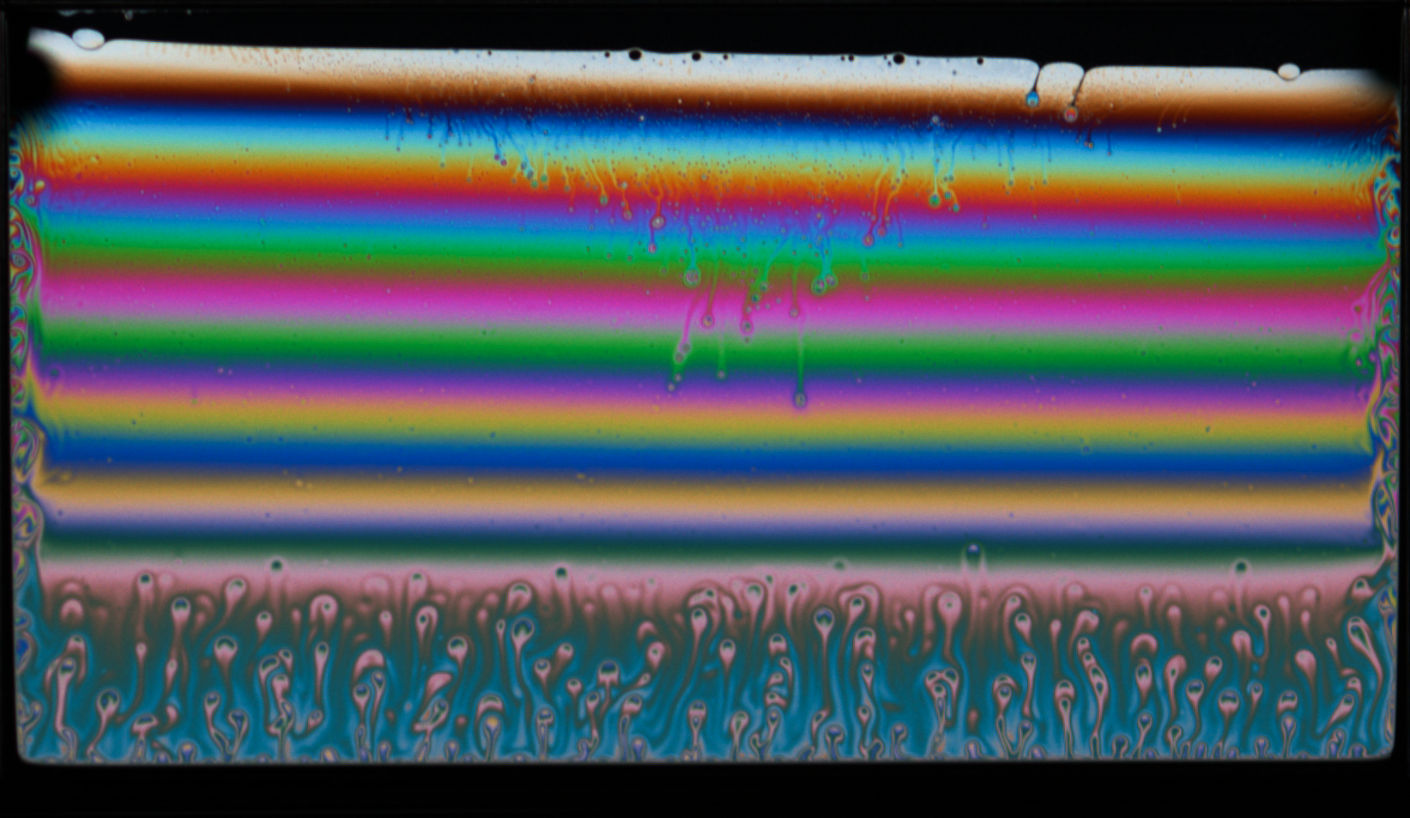
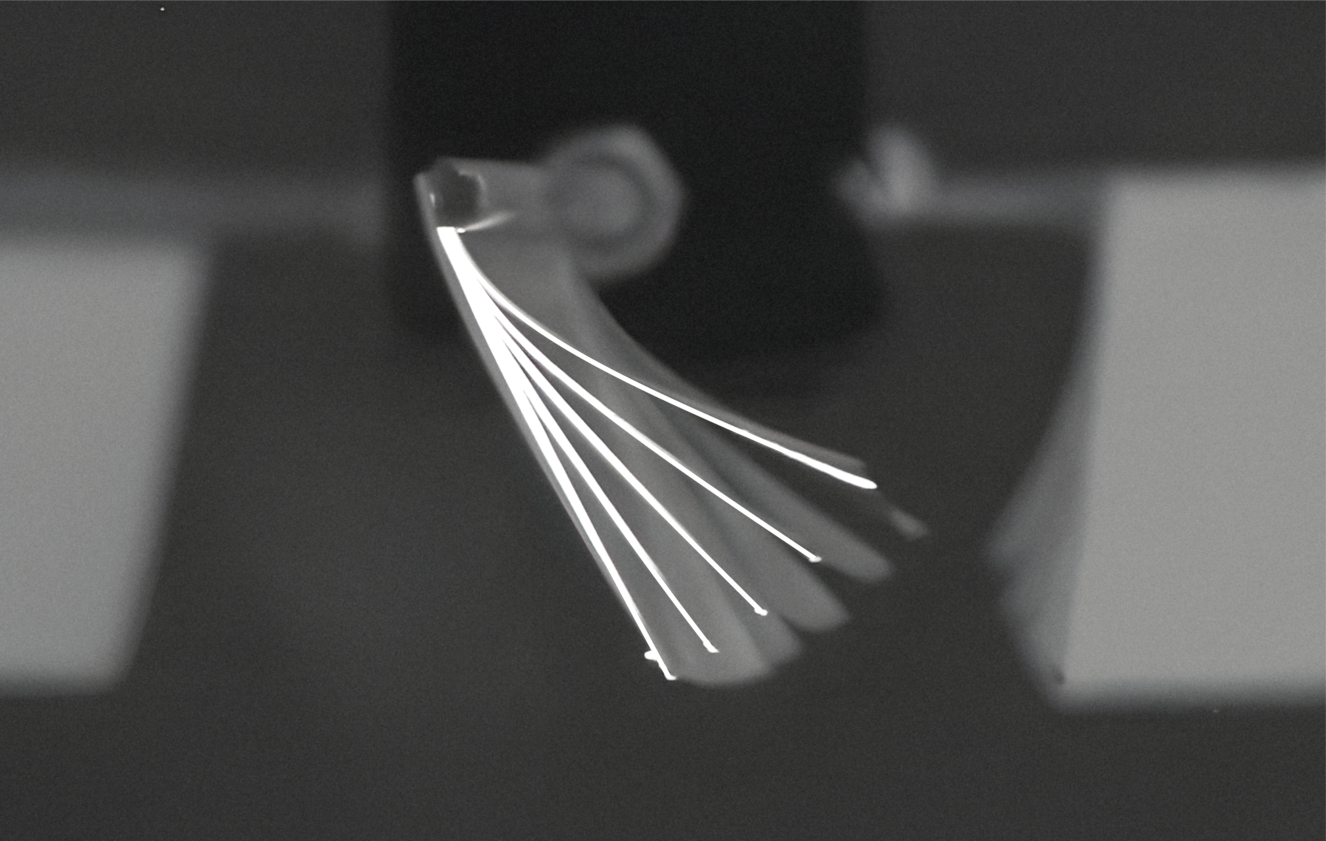
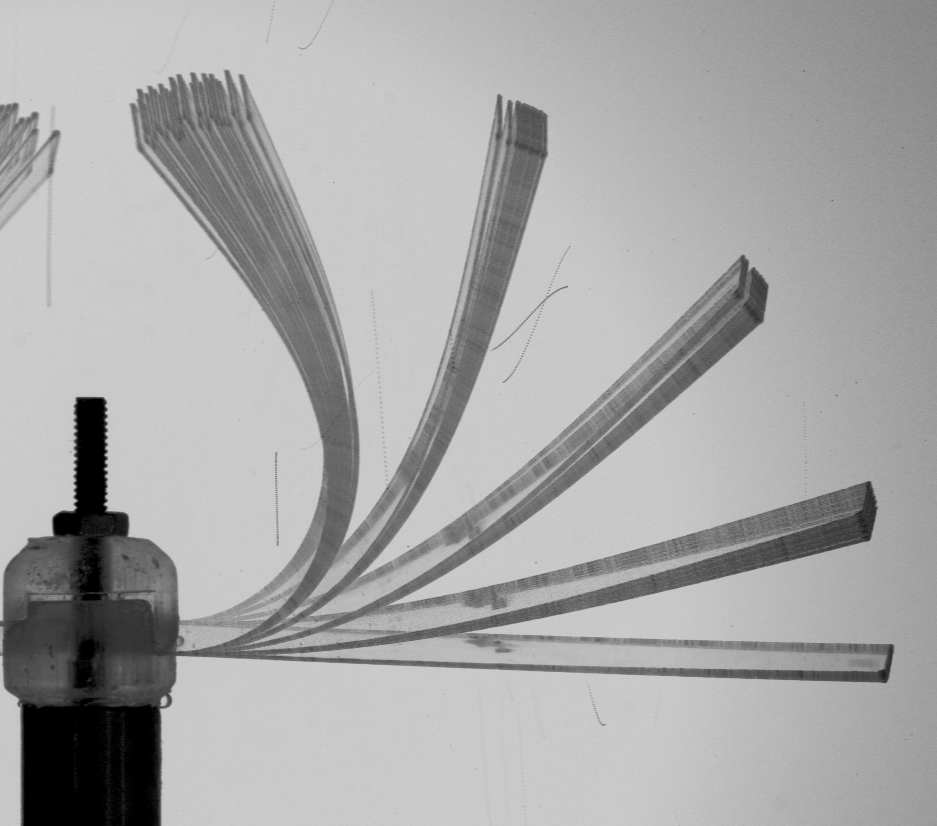
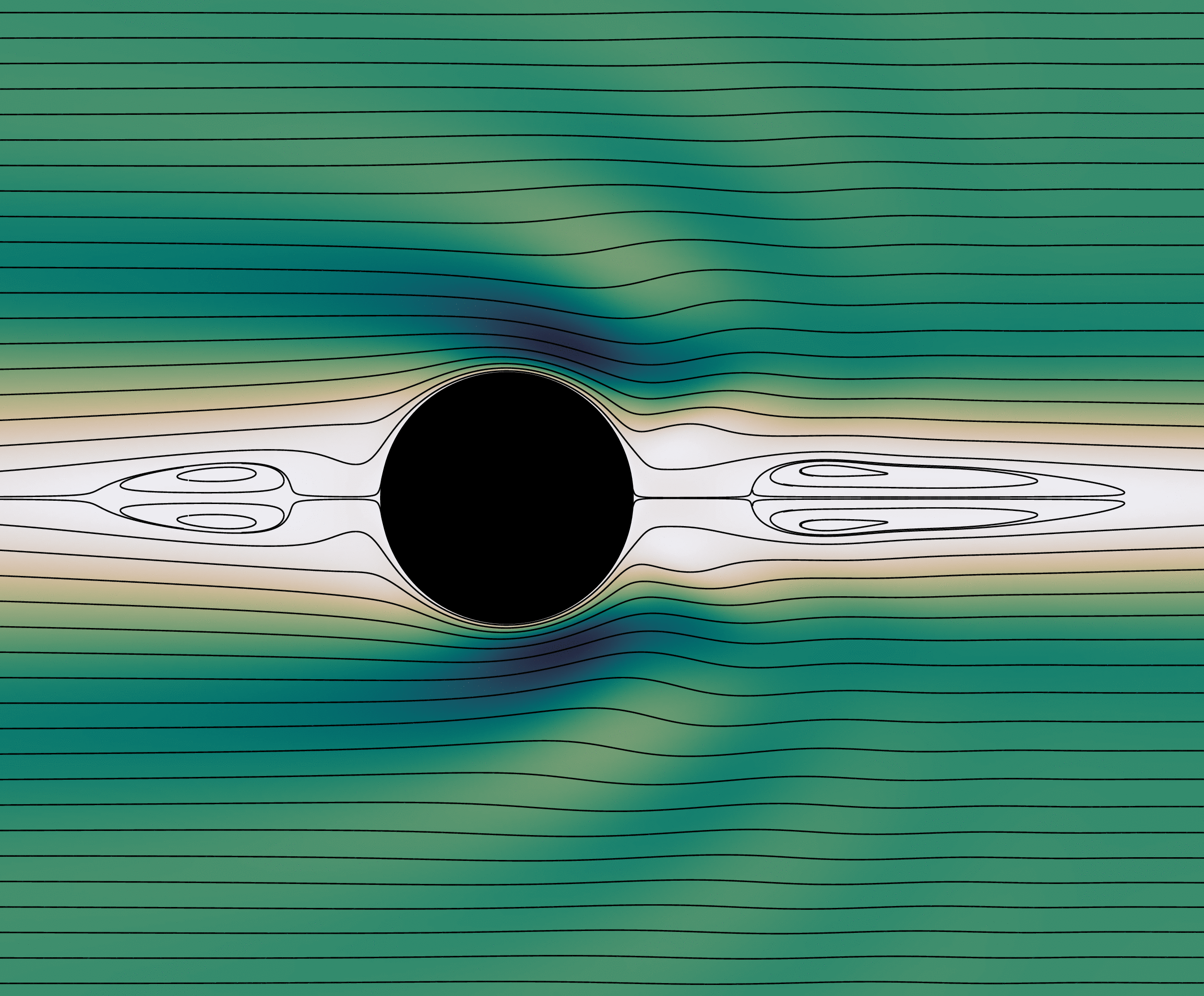
Size Amplification of Jet Drops due to Insoluble Surfactants
Collaborative experimental and numerical study on the jet drops produced by the collapse of a bubble covered with insoluble surfactants. J.E. and T.A. contributed equally to this work.
Eshima, J., Aurégan, T., Farsoiya, P. K., Popinet, S., Stone, H., & Deike, L. (2025)